All the project details are present here. Check and find suitable project here
These each piece of copper wire is a unique bus and can carry data in the form of digital pulses
BUS
A bus can either allow signals to be transferred between devices, the summing (mixing) of output signals from the devices or the distribution of input signals or power amongst the devices. A bus often takes the form of a wire or printed circuit conductor that terminate at multiple connectors which allows the devices to be plugged into the bus.

PCI-X
is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI Local Bus for higher bandwidth demanded by servers. It is a double-wide version of PCI, running at up to four times the clock speed, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation and uses the same protocol.It has itself been replaced in modern designs by the similar-sounding PCI Express, which features a very different logical design, most notably being a "narrow but fast" serial connection instead of a "wide but slow" parallel connection.

PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) Officially abbreviated as PCIe (orPCI-E, as it is commonly called), is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP standards. PCIe 2.1 is the latest standard for expansion cards that is available on mainstream personal computers. PCI Express is used in consumer, server, and industrial applications, as a motherboard-level interconnect (to link motherboard-mounted peripherals) and as an expansion card interface for add-in boards. A key difference between PCIe and earlier buses is a topology based on point-to-point serial links, rather than a shared parallel bus architecture.
Universal Serial Bus

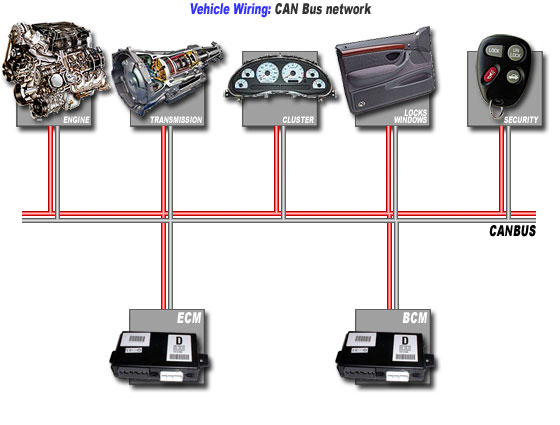
Controller–area network (CAN or CAN-bus) is a vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other within a vehicle without a host computer. CAN is a message based protocol, designed specifically for automotive applications but now also used in other areas such as industrial automation and medical equipment. Development of the CAN-bus started originally in 1983 at Robert Bosch GmbH. The protocol was officially released in 1986 at the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) congress in Detroit, Michigan. The first CAN controller chips, produced by Intel and Philips, came on the market in 1987. Bosch published the CAN 2.0 specification in 1991.
A Soviet ZX Spectrum clone developed in 1991 in Moscow by Kondor and Kramis. It has Z80 at 7 MHz, up to 1024 KiB RAM, 64 KiB ROM, Centronics, AY8910 cound chip, Beta 128 disc interface, IDE interface, and 512x240 multicolor (i.e. 2 colors per 8x1 block) graphics mode for CP/M. Users liked to plug in two 8-bit DACs to play 4-channel modules of Scream Tracker. It was possible to run CP/M and a graphics mode with 512x240 pixels was added to be able to run 80 characters per row. It has both parallel and serial ports, sound processor and the possibility to use an IBM keyboard. In later issues it also had a hard disk interface and turbo mode.Profi

RS-485
, is a standard defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in balanced digital multipoint systems. The standard is published by the ANSI Telecommunications Industry Association/Electronic Industries Alliance (TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the EIA-485 standard can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multi-drop configuration. These characteristics make such networks useful in industrial environments and similar applications.

FireWire The original release of IEEE 1394-1995 specified what is now known as FireWire 400. It can transfer data between devices at 100, 200, or 400Mbit/s half-duplex data rates (the actual transfer rates are 98.304, 196.608, and 393.216 Mbit/s, i.e. 12.288, 24.576 and 49.152 megabytes per second respectively). These different transfer modes are commonly referred to as S100, S200, and S400. Cable length is limited to 4.5 metres (14.8 ft), although up to 16 cables can be daisy chained using active repeaters; external hubs, or internal hubs are often present in FireWire equipment. The S400 standard limits any configuration's maximum cable length to 72 metres (236 ft). The 6-circuit connector is commonly found on desktop computers, and can supply the connected device with power. The 6-circuit powered connector, now referred to as an alpha connector, adds power output to support external devices. Typically a device can pull about 7 to 8 watts from the port; however, the voltage varies significantly from different devices.Voltage is specified as unregulated and should nominally be about 25 volts (range 24 to 30). Apple's implementation on laptops is typically related to battery power and can be as low as 9 V and more likely about 12 V.

LAN

BLUETOOTH

Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is the use of an object (typically referred to as an RFID tag) applied to or incorporated into a product, animal, or person for the purpose of identification and tracking using radio waves. Some tags can be read from several meters away and beyond the line of sight of the reader. Radio-frequency identification comprises interrogators (also known as readers), and tags (also known as labels). Most RFID tags contain at least two parts. One is an integrated circuit for storing and processing information, modulating anddemodulating a radio-frequency (RF) signal, and other specialized functions. The second is an antenna for receiving and transmitting the signal. There are generally three types of RFID tags: active RFID tags, which contain a battery and can transmit signals autonomously, passive RFID tags, which have no battery and require an external source to provoke signal transmission, and battery assisted passive (BAP) RFID tags, which require an external source to wake up but have significant higher forward link capability providing great read range.

RFID SIZE

MIFARE
is the NXP Semiconductors (a spin-off company formed out of Philips Semiconductors)-owned trademark of the reputedly most widely installed contactless smartcard, or proximity card, technology in the world with (according to the producer) over 1 billion smart card chips and 10 million reader modules sold. The patented technology is owned by NXP Semiconductors, with its headquarters in Eindhoven, the Netherlands, and main business sites in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, and Hamburg, Germany

ZigBee
is a specification for a suite of high level communication protocols using small, low-power digital radios based on the IEEE 802.15.4-2003standard for wireless personal area networks (WPANs), such as wireless headphones connecting with cell phones via short-range radio. The technology defined by the ZigBee specification is intended to be simpler and less expensive than other WPANs, such as Bluetooth. ZigBee is targeted at radio-frequency (RF) applications that require a low data rate, long battery life, and secure networking.

Wi-Fi (pronounced /ˈwaɪfaɪ/) is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance that may be used with certified products that belong to a class of wireless local area network (WLAN) devices based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. Because of the close relationship with its underlying standard, the term Wi-Fi is often used as a synonym for IEEE 802.11 technology. The Wi-Fi Alliance is a global, non-profit association of companies that promotes WLAN technology and certifies products if they conform to certain standards of interoperability. Not every IEEE 802.11-compliant device is submitted for certification to the Wi-Fi Alliance, sometimes because of costs associated with the certification process, and the lack of the Wi-Fi logo does not necessarily imply a device is incompatible with Wi-Fi devices.

WIFI Towers
